
State of the Industry Report: Smart Protein in India
In our detailed report, you’ll get current insights into the state of the smart protein industry including: commercial landscape, consumer and investment insights, technical advancements, and regulatory updates.

Executive summary
The smart protein sector in India has seen immense development over the past five years. From a novel category that was unheard of until 5 years ago, it has now struck discourse across businesses, consumers, investors, and the government.
At a time when India’s agricultural sector stands at a critical juncture of sustaining viable and enduring livelihoods for millions of smallholder farmers and providing food and nutritional security to a rapidly growing population, this report showcases how smart protein can be a beacon of hope. An exhaustive compilation of business developments, key technologies, policy updates, and scientific breakthroughs in India over the past five years, this report is a first-ever deep dive into the major highlights from 2021 through April 2023.
Report highlights
Commercial landscape
Key insights:
- The first wave of India’s smart protein startup ecosystem occurred around 2020 when popular brands like GoodDot, Blue Tribe Foods, and Shaka Harry rose to success. The second wave was between 2021 and 2023 with about 113 startups active across plant-based, fermented, and cultivated proteins and a network of 100+ companies supporting its growth.
- The Indian HoReCa industry is poised to reach a market potential of ~₹23.31 trillion ($280 billion) by 2025. While the smart protein category is new, over 500 standalone restaurants and hotels in the top eight Indian cities have launched plant-based menus or dishes over the last few years across various food service platforms.
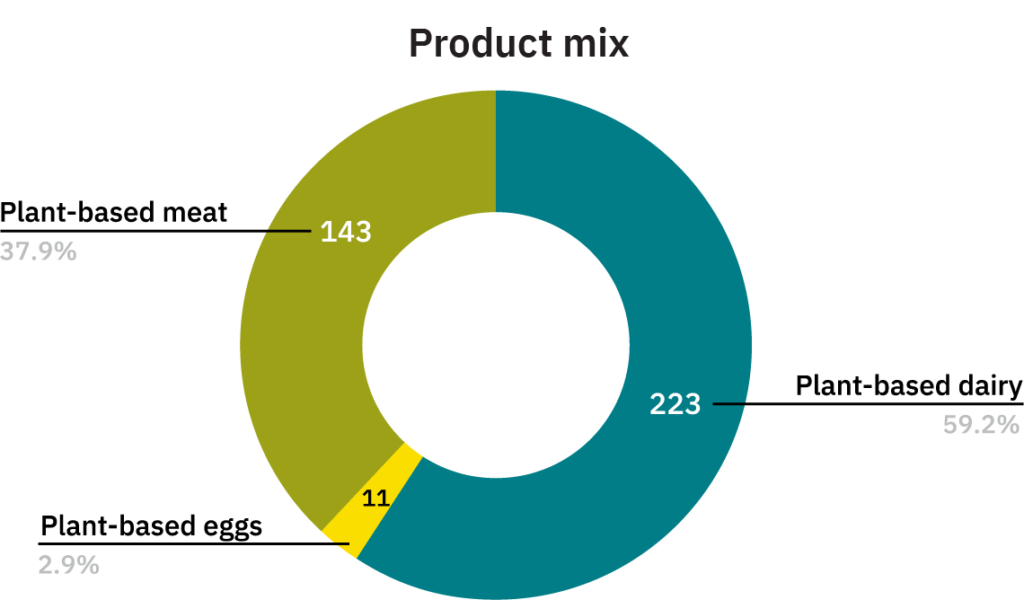
- There are 377 products, across 41 formats, and 73 smart protein brands across meat, eggs, and dairy available in retail and on e-commerce channels. Some brands have also exclusively taken the food service route, with their products only available at select restaurants, hotels, and QSRs.
- There are 143 plant-based meat products, 223 dairy products, and 11 egg products in the market.
Consumer insights
Key insights:
- The early adopters of plant-based proteins in India are predominantly young professionals aged 25–44, living in urban areas, and earning higher incomes (₹50,000+ monthly). This demographic values innovation and aligns smart protein consumption with health and sustainability.
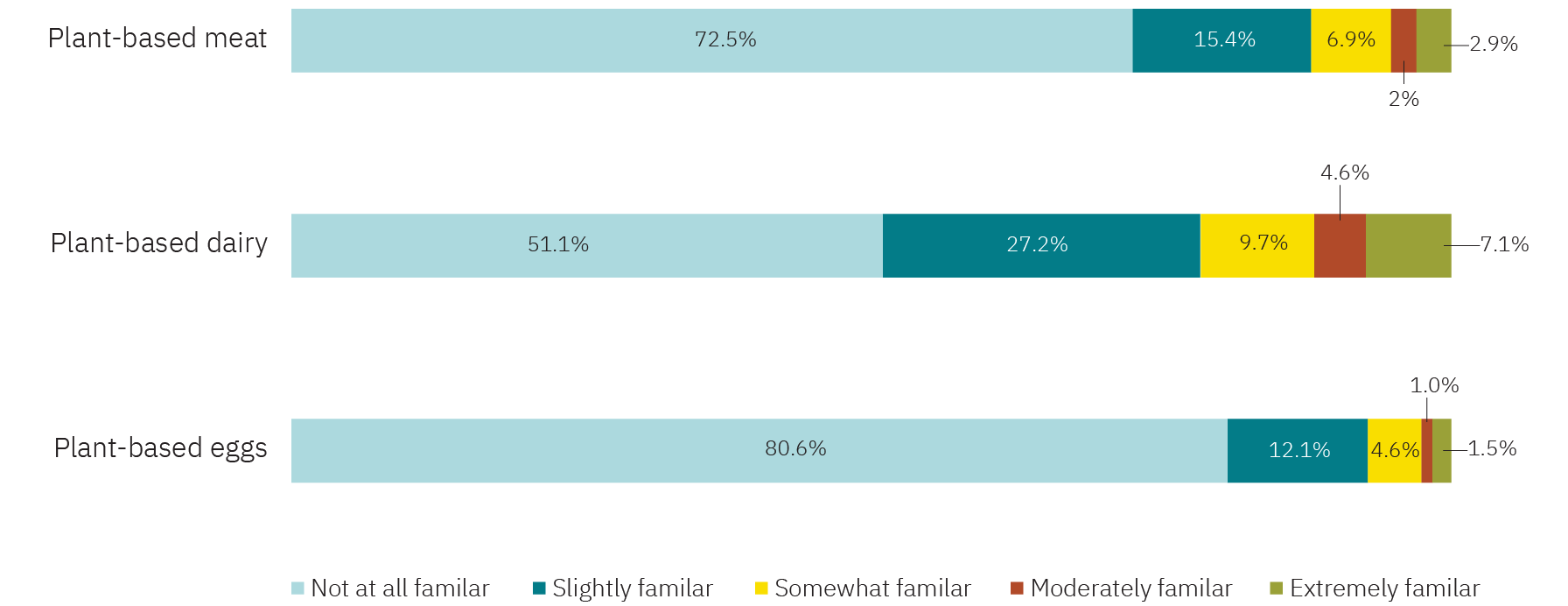
- While 30% of early adopters are aware of plant-based meat and 50% know about plant-based dairy, only 10% and 23%, respectively, have tried these products. This gap reflects both untapped potential and consumer hesitation.
- Health and nutrition claims (e.g., “high protein” and “zero cholesterol”) drive interest more than ethical or environmental motivations like animal cruelty or sustainability. Taste is still a secondary driver for plant-based meat compared to its conventional counterparts.
- Lack of familiarity, resistance from family, and perceived artificiality hinder adoption. Specific challenges include plant-based meat’s “non-juicy texture” and dairy’s limited compatibility with Indian staples like curd or tea.
- High prices relative to conventional options deter many potential consumers, particularly in non-metro areas and mid-income groups. Affordability is essential for broader adoption.
- Products with localised formats—such as kebabs, tikka, or biryani—resonate well with consumers. There’s a clear preference for familiar flavours and formats that fit seamlessly into traditional Indian meals.
- Plant-based proteins often supplement rather than replace conventional meat and dairy. They’re frequently consumed during festivals, religious observances, or specific occasions, rather than as everyday staples.
- Online platforms play a critical role in discovery and accessibility for urban consumers. However, limited offline presence restricts reach, especially in smaller towns.
- Among those who have tried plant-based proteins, a significant majority (72% for meat, 82% for dairy) express intent to repurchase, indicating satisfaction with product offerings.
- There’s a need for strategic awareness campaigns to bridge the knowledge gap, highlight the benefits of plant-based options, and make the category more relatable. Efforts can draw lessons from successful campaigns for milk or eggs in India.
Investments
Key insights:
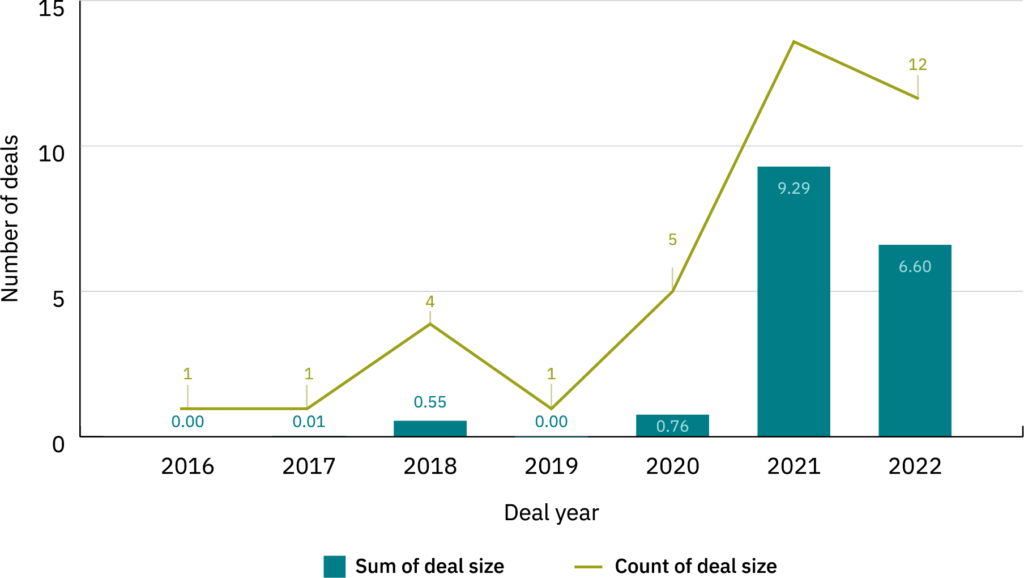
- Globally, the alternative protein sector has attracted $14.2 billion in the last decade, with a notable surge in investments outside North America, representing 58% of total funding in 2022. However, India’s share remains modest, with only $17 million invested in 2021 and 2022.
- High-interest categories include precision and biomass fermentation, alternative fats, and cultivated dairy and seafood. India’s existing biopharmaceutical and fermentation capabilities position it well to capitalise on these opportunities.
- Between 2016 and April 2023, 34 venture capital funds, 27 angel investors, and multiple corporates and grant organisations invested in the sector. Prominent accelerators, like Better Bite Ventures and Ahimsa VC, are supporting startups in scaling operations.
- Companies like Tata, ITC, and Haldiram’s have entered the alternative protein space. Collaborative initiatives, such as setting up food-tech parks, further underline India’s role in global smart protein manufacturing.
- The lack of advanced R&D infrastructure and skilled talent hampers early-stage startups. Enhanced technical mentorship and public-private funding mechanisms are crucial for scaling up.
- Government incentives and concessional finance models are necessary to offset risks, establish infrastructure, and foster large-scale adoption of smart protein technologies.
Science and technology
Key insights:
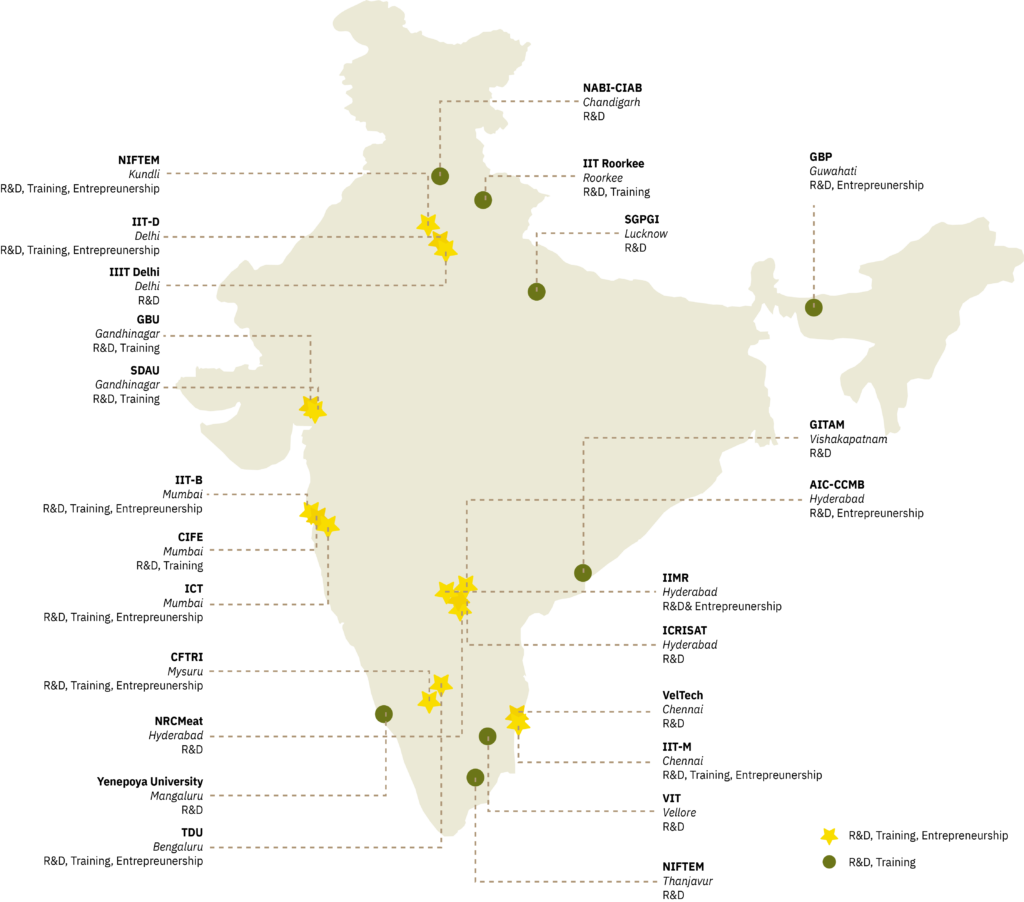
- Public-private partnerships (PPP) have accelerated ingredient and product innovation, particularly in the plant-based sector.
- Fermentation technologies are a cornerstone of India’s smart protein innovation, supported by expertise in biomanufacturing. Companies like Laurus Bio are producing precision fermentation ingredients, such as growth factors for cultivated meat.
- Crop optimisation focuses on enhancing protein-rich pulses, millets, and other indigenous crops to diversify plant-based ingredients.
- Emerging technologies, including 3D food printing and ultrasound processing, are improving texture, flavour, and stability in alternative proteins.
- The Alt Protein Project and other initiatives are fostering talent development to scale innovation in the sector.
- Agencies like DBT and BIRAC have provided funding and support to smart protein projects, reinforcing India’s potential as a global biomanufacturing hub.
Government and regulation
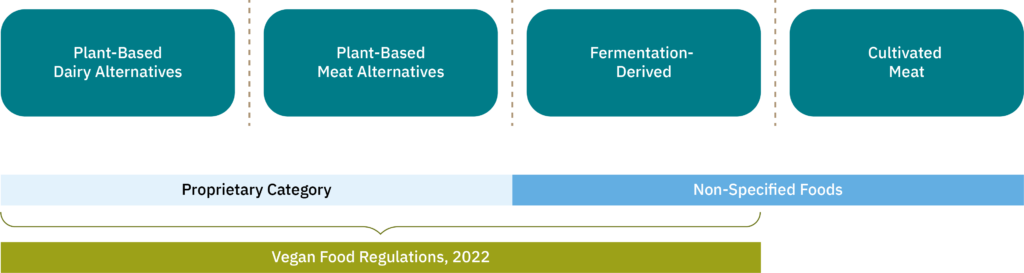
Key insights:
- Government support is critical to the development of the smart protein sector in India, with public funding driving open-access research and regulatory frameworks providing market pathways.
- The Department of Biotechnology (DBT) has set a target for India to become a top-five global biomanufacturing hub by 2025, including smart proteins in its policy roadmap to drive investments, research, and talent creation.
- The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) has made strides in regulatory frameworks, including approvals for plant-based and fermentation-derived products, but cultivated meat awaits further regulatory clarity.
- Maharashtra aims to establish smart protein manufacturing hubs, focusing on farmer integration and leveraging local crops for plant-based protein value chains.
- The Ministry of Food Processing Industries (MoFPI) supports startups under initiatives like Pradhan Mantri Kisan Sampada Yojana, focusing on local manufacturing and infrastructure development.
- APEDA, under the Ministry of Commerce, has launched the National Programme on Vegan Products to position India as a global leader in plant-based exports.
- There is significant potential for state governments to incorporate smart protein into biotechnology and food processing policies, fostering sustainable agriculture and economic development.
