From India to the world: The export opportunity for smart proteins
This report provides guidance for Indian companies looking to export plant-based alternatives by mapping opportunities in key international markets and outlining their regulatory frameworks.

Overview
The plant-based meat sector, currently valued at USD 7 billion, is anticipated to grow significantly, with estimates ranging from USD 88 billion to USD 368 billion by 2035. Germany, the UK, the U.S., Australia, Singapore, and the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) are key export markets for Indian plant-based products based on their current market size, future potential, and government interest.
This report offers a detailed analysis of each of these markets, covering:
- Market size: Current retail and food service sales of plant-based foods
- Consumer profile and demand: Data on vegan, vegetarian, and flexitarian populations and consumer trends in meat consumption reduction and buying habits
- Plant-based product formats in the market: Common storage conditions (refrigerated, frozen, shelf-stable), protein types (beef, chicken, pork), and specific product formats (sausages, burgers, nuggets)
- Key players in the market: Notable local and international brands, along with established conventional meat producers and consumer packaged goods companies entering the plant-based segment
- Key channels: Major retail formats (supermarkets, discount stores, online grocers) and food service distribution channels (wholesalers, specialised distributors, catering companies)
- Key brand partnerships: Examples of international and Indian brands collaborating with local retailers, food service providers, and manufacturers
- Key distributors, manufacturers, and retailers: Major players in the supply chain
- Regulatory overview: Information on legislative authorities, food laws, labelling rules (including restrictions on meat and dairy terms for plant-based products), GMO rules, import-export portals, business registration requirements (such as EORI and USFDA), and tariff benefits, as well as additional guidelines for fermentation-derived and cultivated meat
Key insights
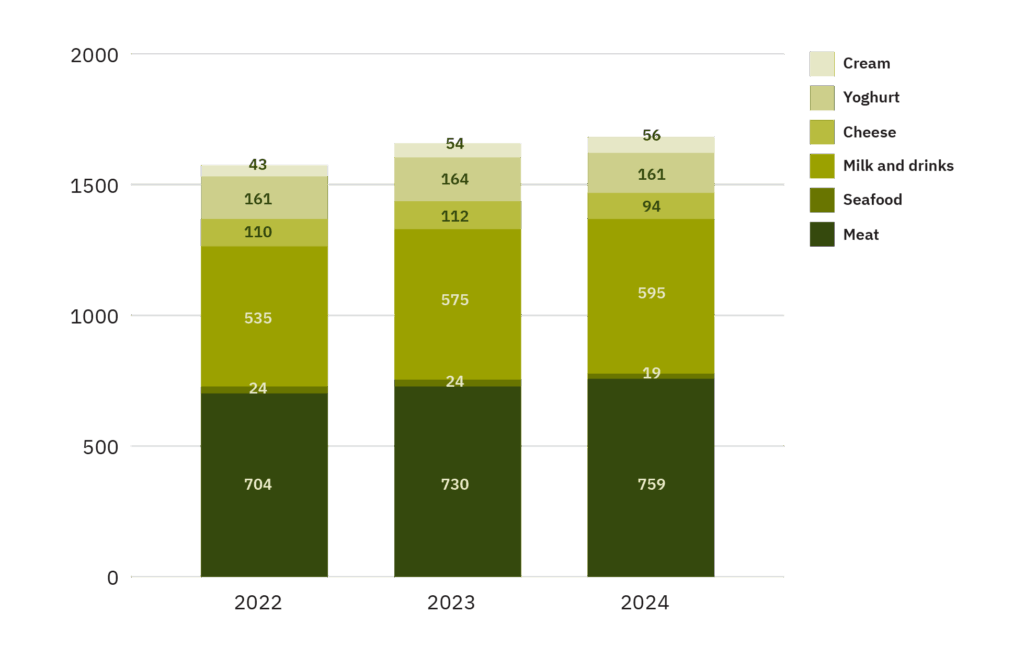
- Germany stands as Europe’s largest plant-based market, valued at €1.7 billion in 2024. Out of this, plant-based meat sales recorded a sales value of EUR 759 million, largely fuelled by private-label offerings and robust retail integration.
- 41% of Germans identify as flexitarian. In 2024, 32% of German households purchased plant-based meat alternatives at least once, and 15% made multiple purchases reflecting steady growth in consumer engagement over the past three years.
- Both major retailers and Quick Service Restaurants (QSRs) like Burger King and KFC have successfully brought plant-based options into the mainstream. Private-label products alone constituted 38.5% of the sales volume in 2024.
- Schnitzels, medallions, meatballs, and slices/strips/cubes are the key product formats in the market.
Key insights
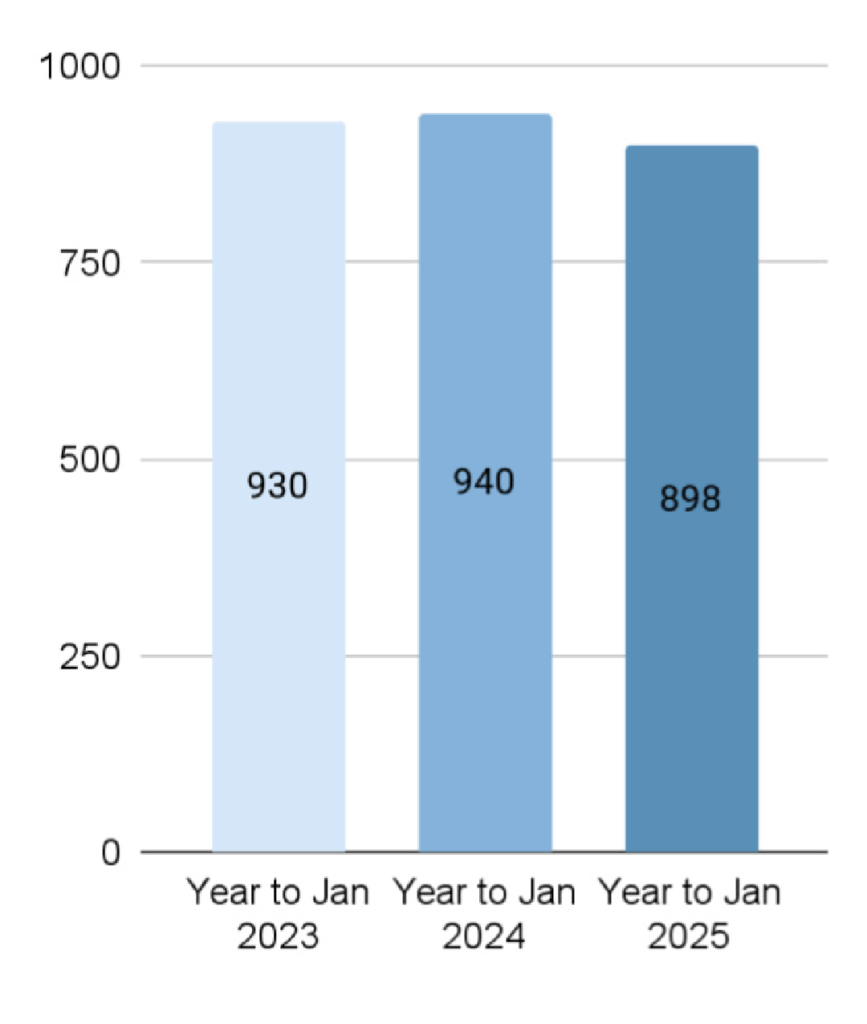
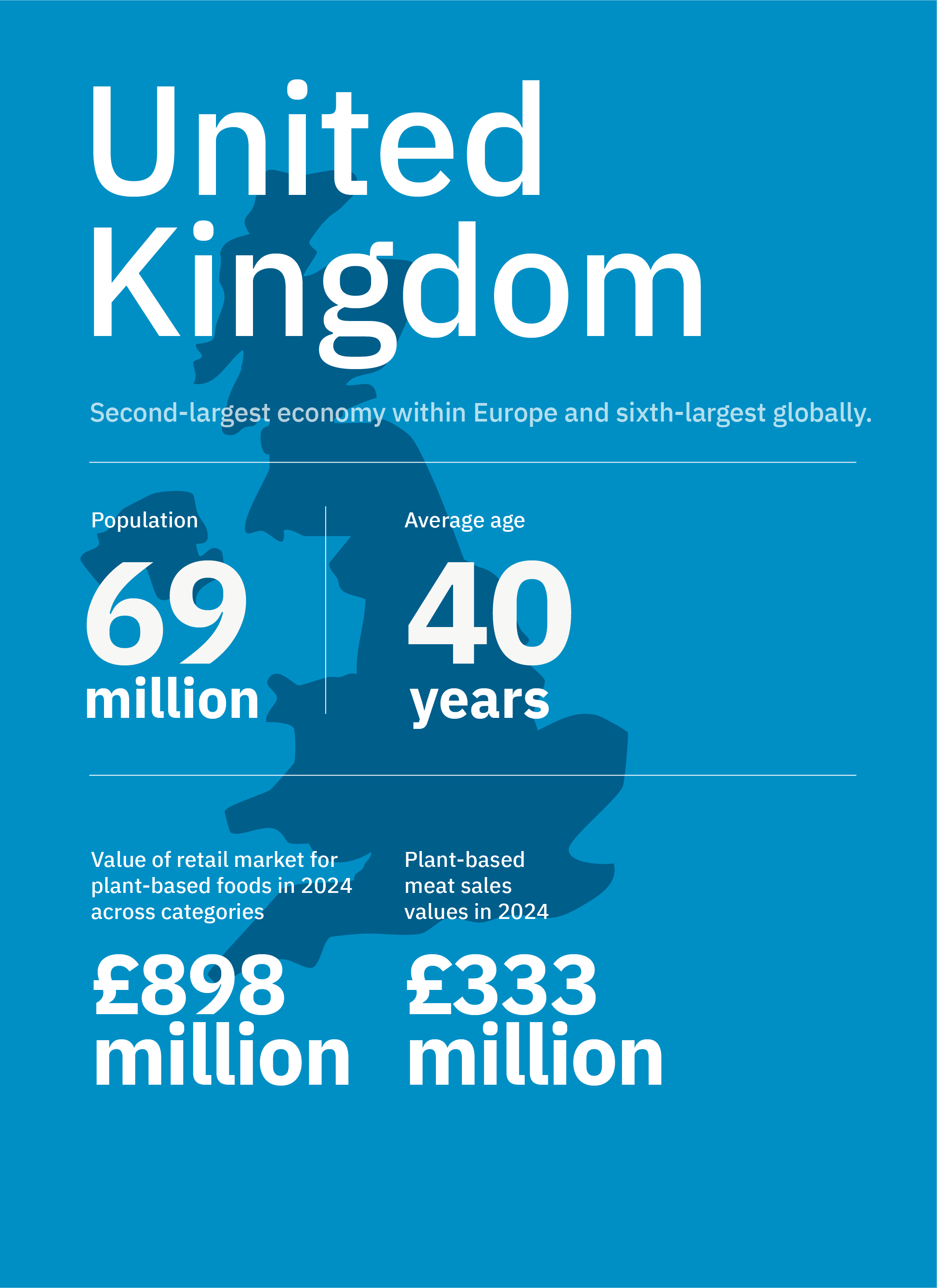
- The UK is the second largest market for plant-based alternatives in Europe, with the plant-based food segment valued at £898 million in 2024, of which plant-based meat accounts for £333 million.
- 3% of consumers are vegan, 3% are vegetarian, and 48% are flexitarian. 31.6% of households purchased plant-based meat in 2024, of which 13% were repeat buyers.
- Chicken (31%), pork/ham (37%), and beef (28%) are the primary alternative protein types, and sausages (22%), mince/pieces (23%), breaded/center-plate (12%), and burgers (11%) are the key product formats in the market.
Key insights
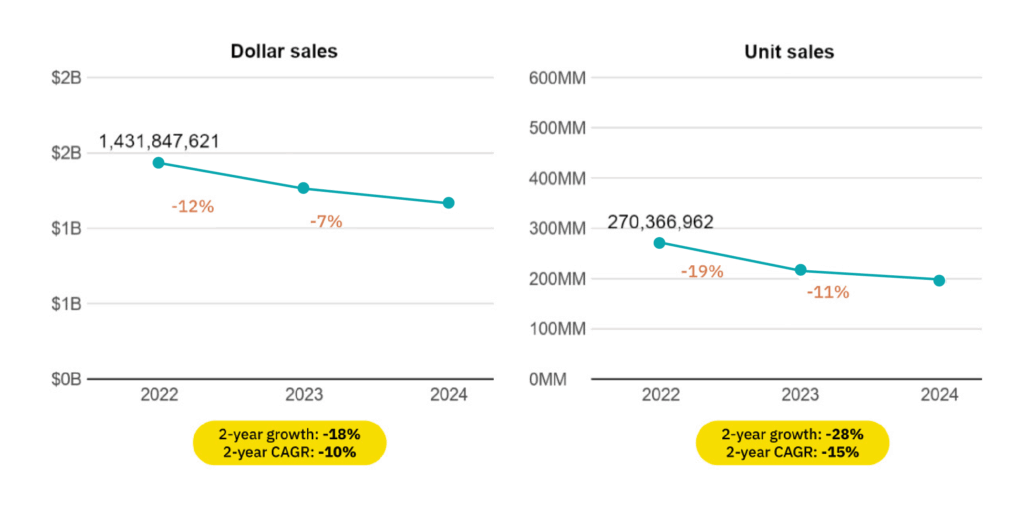
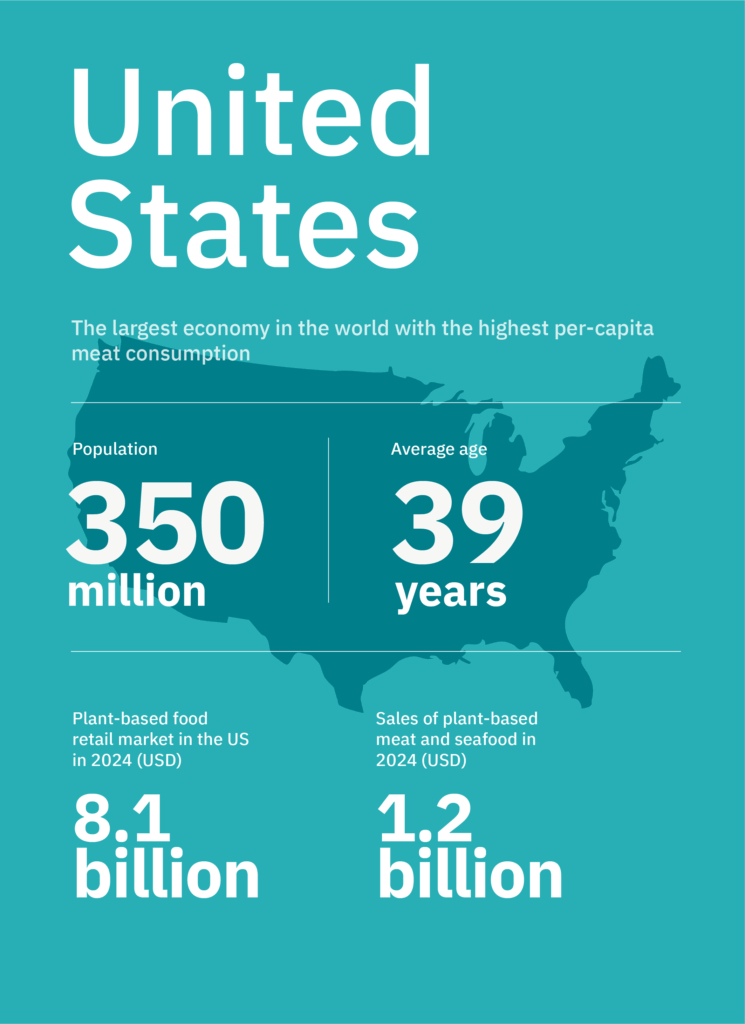
- The United States is one of the largest global markets, with plant-based meat sales valued at around USD 1.2 billion in 2024.
- Over 40% of consumers in the U.S. are reducing meat intake, driven largely by health reasons.
- Plant-based meat and seafood products were purchased by 13% of households in 2024, and 63% of them made multiple purchases within the category.
- Beef is the highest consumed alternative protein type, followed by chicken and pork alternatives. Patties, nuggets, grounds, hot dogs, and breakfast links are some of the key product formats in the market.
- The highest value of sales of plant-based meat are seen within the hotel/restaurant/café (HORECA) sectors, accounting for 53.4% of the total plant-based meat sales revenue in 2024. Quick service restaurants (QSRs) continue to hold a dominant position in the U.S. food service market, holding ~50% of the market share in 2024, followed by full-service establishments, cafés, bars, and cloud kitchens.
Key insights
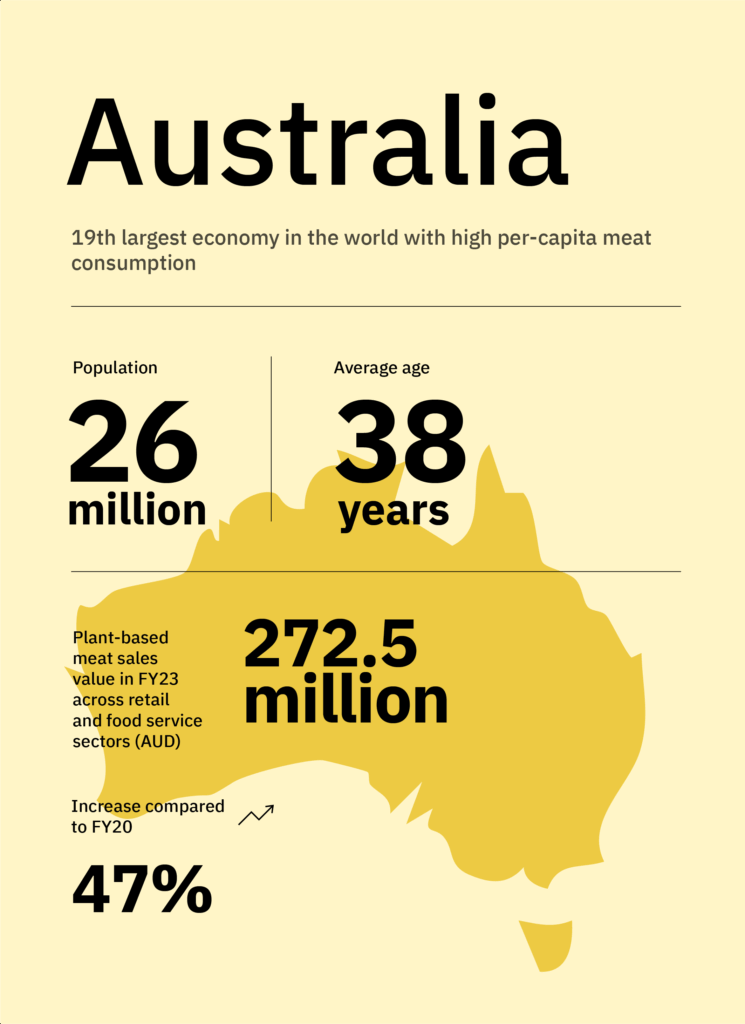
- The Australian plant-based meat market was valued at AUD 273 million in 2023, ranking among the fastest-growing markets in Asia-Pacific.
- According to The Food Frontier consumer survey of 2024, 79% of Australians abstain from consuming meat at least one day per week, with some individuals eliminating it from their diets entirely. 35% of Australians have sampled plant-based meats, an increase from 24% in 2021 driven by health, sustainability, and ethical motivations.
- Crumbed chicken, burgers, mince, sausages, snacks, finger foods, deli slices, and ready meals are the key product formats in the market.
Key insights
- The plant-based meat market in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) is projected to experience substantial growth, increasing to approximately USD 500 million by 2030 (from USD 60 million in 2023), driven largely by the expatriate population and governmental efforts to improve self-sufficiency and food security.
- One-third of consumers are considering replacing meat with plant-based alternatives, especially in fast-food contexts, with the UAE expected to lead with a notably high rate of plant-based meat adoption.
- Prince Khaled bin Alwaleed bin Talal Al Saud of Saudi Arabia actively promotes plant-based lifestyles and has invested in numerous companies in the plant-based sector, including Beyond Meat, Memphis Meats, TurtleTree Labs, and BlueNalu, through his KBW ventures.
- In the GCC, poultry is the primary meat consumed, unlike in Western countries. Consequently, there is a greater opportunity for plant-based chicken alternatives compared to plant-based beef.
- Halal certification is mandatory for market entry in this region. While vegan ingredients are inherently halal, plant-based meat manufacturers are increasingly pursuing halal certification to improve confidence among Muslim demographics.
- Western formats such as burger patties, sausages, nuggets, and mince are popular choices among the youth. Plant-based versions of regional dishes such as kebabs, koftas, shawarma, shish tawook, kibbeh, and kabsa, among others, are also a growing trend.
Key insights
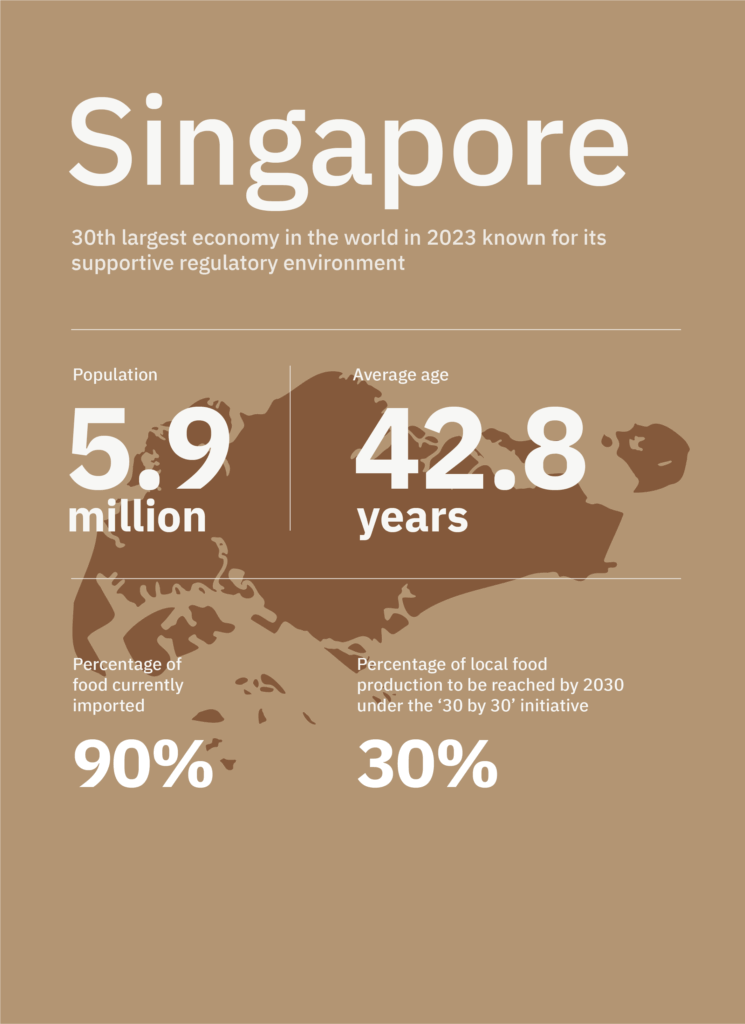
- Around 7% of the population in Singapore follow vegetarian or vegan diets. In a 2020 survey, ~39% of Singaporeans identified as flexitarians.
- Singapore’s top reason for considering a plant-based diet is health concerns (46%), followed by health risks of meat/fish production (37%), the healthiness of processed meat (32%), and environmental reasons (24%).
- To improve food security, Singapore aims to reach 30% of local food production by 2030 under the ‘30 by 30’ initiative. The government actively supports the alternative protein industry through conducive regulatory frameworks for cultivated meat and incentives for global food corporations to establish research and development centres, new product development facilities, and pilot projects within Singapore, positioning it as Asia’s R&D and innovation hub for alternative proteins.
- Beef alternatives currently dominate the plant-based meat sector in Singapore. However, pork and chicken alternatives are growing at a rapid pace in line with the region’s meat preferences. Seafood alternatives present a significant opportunity, but relatively, not as much innovation has been seen in this segment.
- Innovation in Asian meat formats is critical to garner consumer interest in Singapore. These include products that are compatible with the local cuisine, consisting of rice or noodles accompanied by stir-fried meat, vegetables, or gravies/sauces.